
Consumer Electronics
Consumer Electronics PCBA Manufacturer-– Design to Production
Consumer Electronics PCBA Manufacturer of Choice-Rich PCBA
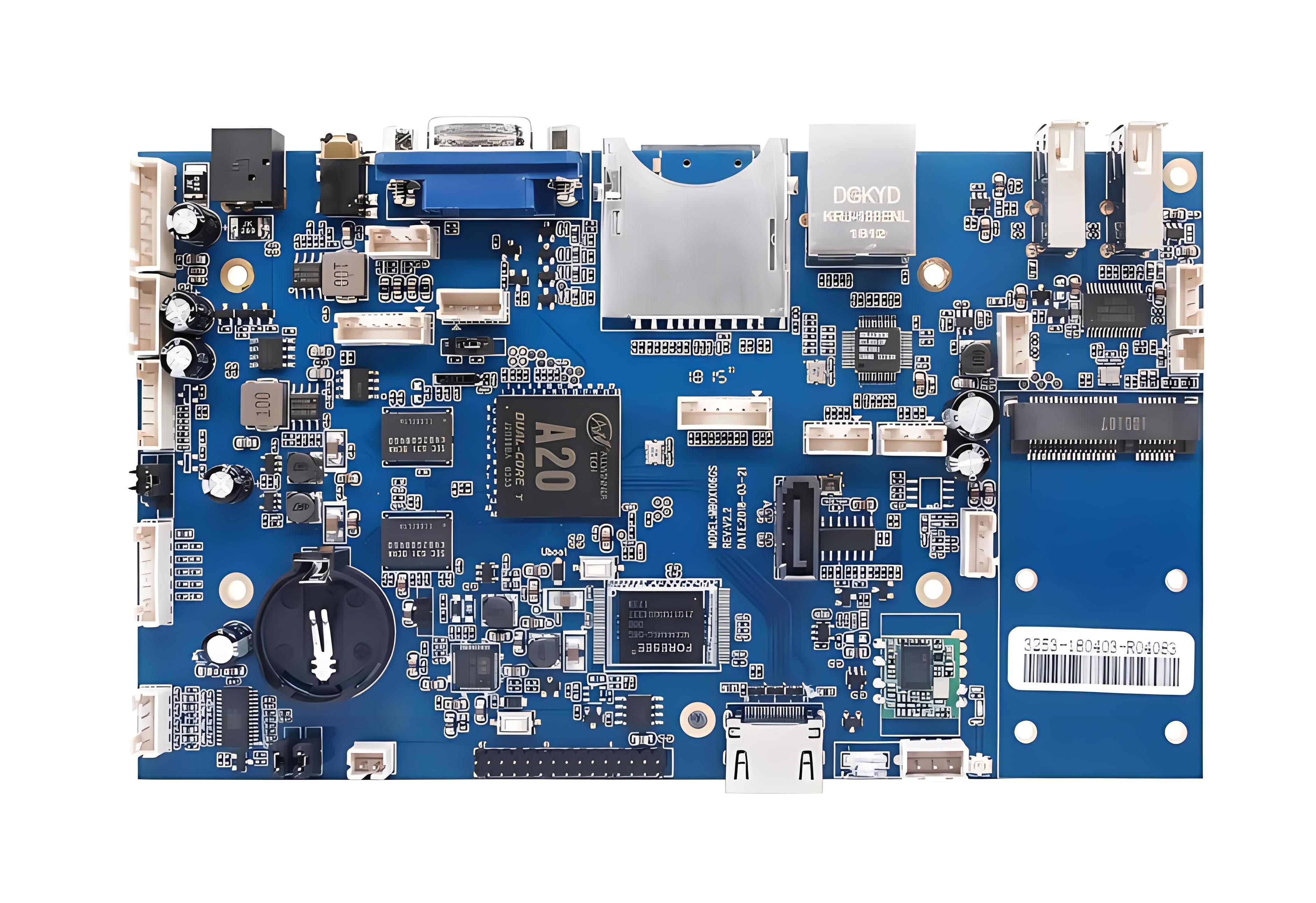
What is Consumer Electronic PCB?
Consumer electronics have become an indispensable part of our daily lives, encompassing electronic devices designed for personal use, entertainment, and communication. These devices include smartphones, tablets, laptops, televisions, game consoles, digital cameras, smartwatches, and other gadgets that are ubiquitous in modern life.
Consumer electronics are usually mass-produced with an emphasis on affordability, ease of use, and aesthetics. The industry is constantly evolving and releasing new products and technologies to meet the changing needs and preferences of consumers. These devices, such as smartphones, laptops, game consoles, and smartwatches, make our lives more convenient and connected, providing us with access to information, entertainment, and communication anytime and anywhere.
Turnkey Consumer Electronics PCBA – Design to Production
Step 1: Understand the key features of consumer electronics circuit
Size and Shape: PCBs for consumer electronics must be designed to fit within small form factor devices, such as smartphones and smartwatches, making compactness and lightweight crucial design considerations. Additionally, they must be designed to accommodate other internal components.
Durability: Consumer electronics are exposed to heat, humidity, and mechanical stress, which can cause wear and tear on the boards. Therefore, higher quality materials are used during manufacturing to ensure they can withstand these conditions.
Power Efficiency: The limited space in compact electronic devices means that energy storage is a challenge. Capacitors and other key components must be small yet powerful. Achieving high power efficiency while minimizing power consumption is key.
Complexity: With more components being packed into smaller spaces, consumer electronics devices are becoming increasingly complex. This requires PCBs to be designed to handle complex circuits, with multi-layer and high-density designs becoming more common.
Step 2: Design and plan circuit layout
PCB Design: A crucial element in ensuring high production quality. Well-designed PCBs can improve the performance, reliability, durability, and reduce manufacturing costs of consumer electronics. The design process involves multiple stages, including schematic design, layout design, and Gerber file generation.
Schematic Design: A critical step in realizing the function of the circuit. The process involves selecting appropriate components, designing power circuits, filtering and protection, testing and verification, and ensuring proper layout and wiring.
PCB Layout: A essential to ensure stable function and performance of electronic devices. Key considerations include size and shape, required number of layers, component location, signal integrity, power and ground layout, heat dissipation design, and EMC design.
Gerber File Generation: A necessary for PCB manufacturing. Gerber files contain all the information needed to produce a PCB, including copper track layout, component placement, and drilling. PCB layout software is used to generate Gerber files, which are then used by PCB manufacturers to produce the PCB.
Step 3: Bare board manufacturing and component mounting
Bare-Board Fabrication: It Is the first step for a PCBA company to produce a complete circuit board. It involves preparing the substrate material, usually fiberglass or plastic resin, and coating it with a layer of copper foil. The copper foil is then etched with a chemical solution to remove unwanted copper, leaving the conductive pathways needed to connect the electronic components.
Component Assembly: Follows the bare-board fabrication, where electronic components are mounted on the board. An automated machine is usually used for this process, which picks up the component and places it on the board. The components are then soldered to the board using wave soldering or reflow soldering.
Quality Control: This is an important aspect of the PCBA manufacturing process that needs to be implemented throughout the process to ensure that the PCB meets performance requirements. Any defects found during the process need to be addressed immediately by stopping the process, exploring the cause, and finding a solution to the problem. This is critical to ensure the quality of the final product.
Consumer Electronics PCB Applications
Electronic devices, such as televisions (including LED and LCD screens), home audio systems, speakers, smartphones (both old and new), intercoms, calculators, security cameras, doorbells, electric appliances (e.g., kettles, ovens, stoves, and irons), washing machines, air conditioners, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), electronic locks, proximity sensors, wearable electronics (e.g., smartwatches and smart rings), Bluetooth hands-free sets, optical devices (such as cameras and CCTV), wireless devices (e.g., Bluetooth speakers), remote controls for monitoring water levels, IR sensor-based devices, children’s toys, and e-cigarettes, rely heavily on PCBs, which are hidden within these devices.
Most of these devices utilize rigid PCB, which come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and colors (usually green, but sometimes brown in mass-produced inexpensive electronics). They are commonly used in home automation, kitchen appliances, and other household appliances and are typically single-sided or two-sided to reduce cost and limit functionality. PCBs in less advanced devices (e.g., remote controls, toys, and electric kettles) may not be as complex as those found in more advanced devices such as LED and Smart TVs, which may require multiple layers and complex Flexible PCB, ultimately leading to more expensive products.
Here are some common applications for consumer electronics PCBs:
Smartphones and Tablets: Circuit boards are essential to these devices, providing the platform for microprocessors, memory, sensors, and other electronic components that power these devices and enable them to perform a wide range of functions.
Laptops and Desktops: We are more familiar with the PCBs used in laptops and desktops, such as the motherboard, graphics card, and other internal components that provide the frame for these devices.
Gaming Consoles: Gaming consoles heavily rely on circuit boards to provide processing power and connectivity for online gaming and multimedia applications. The game card used in the Xiaobawang game console, which was popular worldwide in the 1990s, is an example of a low-end circuit board.
Smart Home Devices: Smart home devices, such as thermostats, security cameras, and smart lighting systems, rely on high-density printed circuits to provide the electronic circuitry necessary to communicate with other devices and the internet.
Audio and Video Equipment: Circuit boards are essential to audio and video equipment such as televisions, DVD players, and audio systems, providing the necessary circuitry to process and output audio and video signals.
Automotive Industry: New energy vehicles require more electronic products than traditional fuel vehicles and rely on advanced PCBs for engine management, anti-lock braking systems, car audio, GPS systems, climate control systems, and vehicle infotainment systems, such as control and monitoring systems.
Medical Equipment: Medical equipment, such as MRI machines, heart monitors, and dialysis machines, relies on medical PCB to provide the necessary circuitry to control and monitor the operation of these systems, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data generated by the equipment.
At Rich PCBA, we offer a wide range of services to various consumer electronics industries, including home appliances, entertainment electronics, digital equipment, and more. With extensive manufacturing and assembly capabilities, we ensure that our services meet various tests. Whether you need turnkey consumer electronics PCBA services for prototyping or production, we are here to help.

To learn more about our capabilities or to request a quote, continue reading or contact our office directly.

